Japanese beetles (Popillia japonica) are highly invasive pests of more than 300 plants including some of Idaho’s top commodities. ISDA is currently implementing Japanese beetle eradication plans in two areas of Idaho (Caldwell and Pocatello).
Caldwell Eradication Program
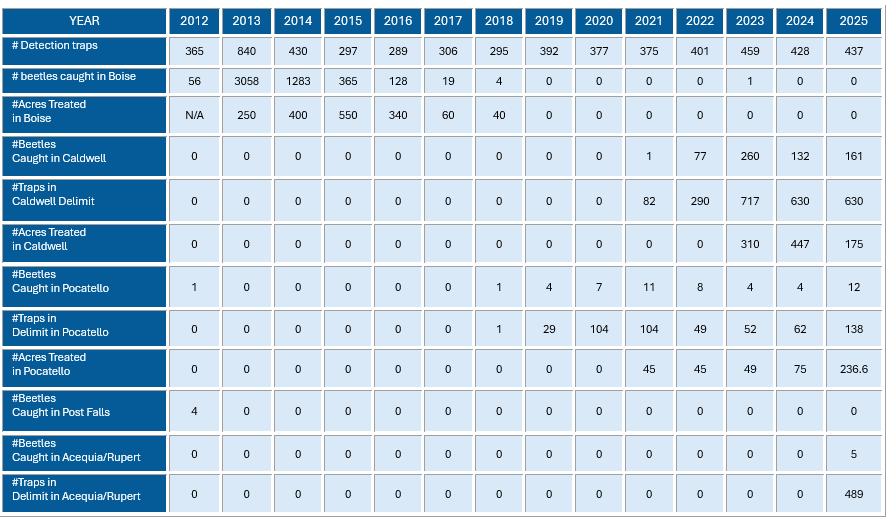
In Caldwell area ISDA’s trap deployment has increased from 82 traps in 2022 to an increased plan of 630 traps in 2026. Treatments for Japanese beetle in the area have decreased from 290 acres in 2024 to 175 acres in 2025.
2021
- Traps deployed: 1 detection trap
- Beetles collected: 1 Japanese beetle specimen
- Location: Canyon County, Caldwell
- Treatment: None
2022
- Traps deployed: 82 traps around the 2021 positive detection site
- Beetles collected: 77 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 20 Positive Sites
- Treatment: None
2023
- Traps deployed: 290 traps to define infestation boundaries
- Beetles collected: 260 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 37 Positive Sites
- Treatment: Two treatments (May and July)
- 115 Acres
2024
- Traps deployed: 717 traps
- Beetles collected: 132 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 39 Positive Sites
- Treatment: Two treatments (May and July)
- 290 Acres
2025
- Traps deployed: 630 delimit traps to ensure no additional infestations were missed
- Beetles collected: 161 Japanese beetles
- Positive trap locations:
- 28 Positive Sites
- Treatment expansion: Two treatments (May and July)
- 175 Acres
2026 (Planned)
- Traps planned: 630 delimit traps to ensure no additional infestations were missed
- Treatment planned: Two treatments (May and July)
- ~85 Acres
Acequia/Rupert Eradication Program
In Acequia ISDA immediately deployed 489 delimit traps following the single detection. A total of 5 beetles were caught between Acequia and Rupert. ISDA plans to increase the traps to 938 and is planning treatments for 2026.
2025
- Initial detection: 1 detection trap in Acequia
- Beetles collected: 1 Japanese beetle specimen
- Location: Minidoka County, Acequia
- Delimit survey response: Following the initial detection, ISDA deployed 489 delimit traps around the Acequia positive
- Positive trap locations:
- 5 Positive Sites
- Additional beetles found: 4 more Japanese beetles caught in traps near the town of Rupert
- Treatment: None
2026 (Planned)
- Traps planned: 938 delimit traps between Acequia and Rupert (increased from 489)
- Treatment planned: Two rounds of Japanese beetle treatment in select areas
Pocatello Eradication Program
In Pocatello area ISDA’s trap deployment has increased from one trap in 2018 to an increased plan of 449 traps in 2026. Treatments for Japanese beetle in the area have also expanded from 45 acres in 2021 to 236.6 acres in 2025.
2018
- Traps deployed: 1 detection trap
- Beetles collected: 1 Japanese beetle specimen
- Location: Bannock County, Pocatello
- Treatment: None
2019
- Traps deployed: 29 traps around the 2018 positive detection site
- Beetles collected: 4 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 4 Positive Sites
- Treatment: None
2020
- Traps deployed: 104 traps to define infestation boundaries
- Beetles collected: 7 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 2 Positive Sites
- Treatment: None
2021
- Traps deployed: 104 traps
- Beetles collected: 11 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 4 Positive Sites
- Treatment: Two treatments (May and July)
- 45 acres
2022
- Traps deployed: 49 traps around the area of concern
- Beetles collected: 8 Japanese beetles in 2 traps at Ross Park
- Positive trap locations:
- 2 Positive Sites
- Treatment: Two treatments (May and July)
- 45 acres
2023
- Traps deployed: 52 traps
- Beetles collected: 4 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 2 Positive Sites
- Treatment: Two treatments (May and July)
- 49 acres
2024
- Traps deployed: 62 traps
- Beetles collected: 4 Japanese beetles (July–September)
- Positive trap locations:
- 3 Positive Sites
- Treatment: Two treatments (May and July)
- 75 acres
2025
- Traps deployed: 138 traps to ensure no additional infestations were missed
- Beetles collected: 12 Japanese beetles
- Positive trap locations:
- 8 Positive Sites
- Treatment: Two treatments (May and July)
- 236.6 acres
2026 (Planned)
- Traps planned: 449 traps to cover the Pocatello area (expanded delimit survey)
- Treatment planned: Two treatments (May and July)
- 129 acres
- Japanese beetles are ½ to ¾ inch long.
- Front of body is shiny metallic green. Wing cases are coppery.
- Body has 5 white tufts of hair along each side.
- Adult beetles feed on the upper leaf surface, removing leaf tissue and releasing an aggregation pheromone that attracts additional beetles to the potential food source.
- Manifested as skeletonized leaves with large, irregular holes, adults will move to devour flowers and fruits.
- Evidence of grub (beetle larva) are often unnoticed until populations build up to levels of sufficient to kill grass roots.
- Evidence of damage is seen when localized discolored patches appear.
- Attracted to some of Idaho’s top commodities including hops, grapes, apples, stone fruits, vegetable crops, and nursery stock.
-




Caldwell
- An established infestation that appears to be centered in a Caldwell residential area bordered by Lincoln Rd (N), Franklin Rd (S), I-84 (W) and Aviation Way (E).
Acequia/Rupert
- In Acequia/Rupert area beetles have been caught South of Hwy 24 (S) of Acequia to Rupert on E 100 N between N 100 E and N 300 E and then on E Baseline Rd.
Pocatello
- In Pocatello beetles have been caught South of (E) Center St to Ross Park on (S) 2 Ave. below South Valley Rd. over to Bannock Hwy near Riverside Golf Course, and North to (S) Grant Ave. New catches are in the area between W Center St. to W Hayden St. between N Grant Ave. and N Lincoln.
Caldwell and Pocatello residents in treatment areas:
- Complete the consent form and return to ISDA by email jb@isda.idaho.gov by April 18, 2025.
- Be on the look out for a notification about treatment, approximately one week before the pesticide application.
Others:
- Look out for signs of Japanese beetle (see “Identifying Japanese Beetles”).
- Report any signs of Japanese beetle to ISDA at JB@ISDA.Idaho.Gov and please provide pictures if you are able.
See the resources below for more information on Japanese beetles in Idaho.
- Pollinator Protection – The Idaho State Department of Agriculture takes extensive measures to ensure that all insect eradication efforts have minimal impact on bees and other pollinators.
- Pesticides Used:
- May application – Granular Insecticide Acelepryn G – active ingredient chlorantraniliprole, is classified by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency as a reduced-risk pesticide. It has the lowest relative toxicity compared to other insecticides labeled for the same purpose.
- Mid-July application – Granular Insecticide Imidacloprid – developed to mimic nicotine which is a naturally occurring compound found in many plants, including tobacco, and is very toxic to insects. Possible hazards to pollinators exist with residue in leaves and blossoms of treated plants. When applied only to turfgrass, strictly adhering to label directions, this neonicotinoid-class pesticide can eliminate the JB grub without harming bee and pollinator health and will remain a critical tool in the eradication effort (National Pesticide Information Center (NPIC), 2010).
“Though these products have excellent safety records with the intended action plan use, ISDA will be taking extraordinary measures to ensure that pesticide applications have minimal impact on residents and the environment.”
Caldwell Treatment Area
- A total of 120 acres of treatable turf is planned for Caldwell in 2026)
- 483 residential or commercial properties 250 acres (estimated 100 acres treatable turf)
- 1 school property 20 acres (estimated 13 acres treatable turf)
- Residents will be notified at least 1 week in advance of any treatment.
- May application – Granular Insecticide Acelepryn G.
- Mid-July application – Granular Insecticide Imidacloprid.
- Each treatment area will take one week but the application of larvicide to each property only takes about 15 minutes.
Acequia/Rupert Treatment Area
- A total of 105 properties and 417 acres of treatable turf is planned for Acequia/Rupert in 2026
- 4 properties owned by Minidoka County estimated 64 acres.
- 101 residential/commercial properties estimated 353 acres.
- Residents will be notified at least 1 week in advance of any treatment.
- May application – Granular Insecticide Acelepryn G.
- Mid-July application – Granular Insecticide Imidacloprid.
- Each treatment area will take one week but the application of larvicide to each property only takes about 15 minutes.
Pocatello Treatment Area
- A total of 298 properties and 129 acres of treatable turf is planned for Pocatello in 2026
- 11 properties owned by City of Pocatello/Bannock County estimated 15 acres.
- 287 residential/commercial properties estimated 114 acres.
- Residents will be notified at least 1 week in advance of any treatment.
- May application – Granular Insecticide Acelepryn G.
- Mid-July application – Granular Insecticide Imidacloprid.
- Each treatment area will take one week but the application of larvicide to each property only takes about 15 minutes.
If not properly eliminated, Japanese beetles have potential to be destructive to Idaho’s agriculture industry.
- The industry would suffer losses due to decreased production of marketable fruit and plant products, increased pesticide use, and loss of markets if other states or countries enacted quarantines against Idaho products.
- Western states and foreign countries could impose quarantine restrictions on movement of Idaho’s top agricultural commodities including hop, apple, grape, stone fruit, vegetable seed, and nursery stock.
Pre-Treatment:
- Your property is accessible to the contractor’s crew. All applicable outside gates and entryways should be unlocked, and animals must be kept inside.
- Non-stationary items that can be easily moved should be removed from lawns and grassy areas.
- Water and food bowls for pets should be removed or covered during application.
- Adults, children and pets of all kinds should remain inside during the application.
Note: Koi ponds and all water features containing fish or other aquatic animals should be tightly covered immediately before application. The cover should be removed immediately after the treatment is completed.
Post-Treatment:
- Thoroughly water lawn and grassy area on your property where the granular turf treatment has been applied to allow it to penetrate the soil where the grubs are feeding.
- After the turf treated areas are watered, allow to dry completely.
- Once the area is dry, people and pets may safely re-enter/ resume normal activities.
*Please use an automated sprinkler or garden hose to water in the granular treatment, DO NOT flood irrigate.
Statewide Monitoring and Treatment Results